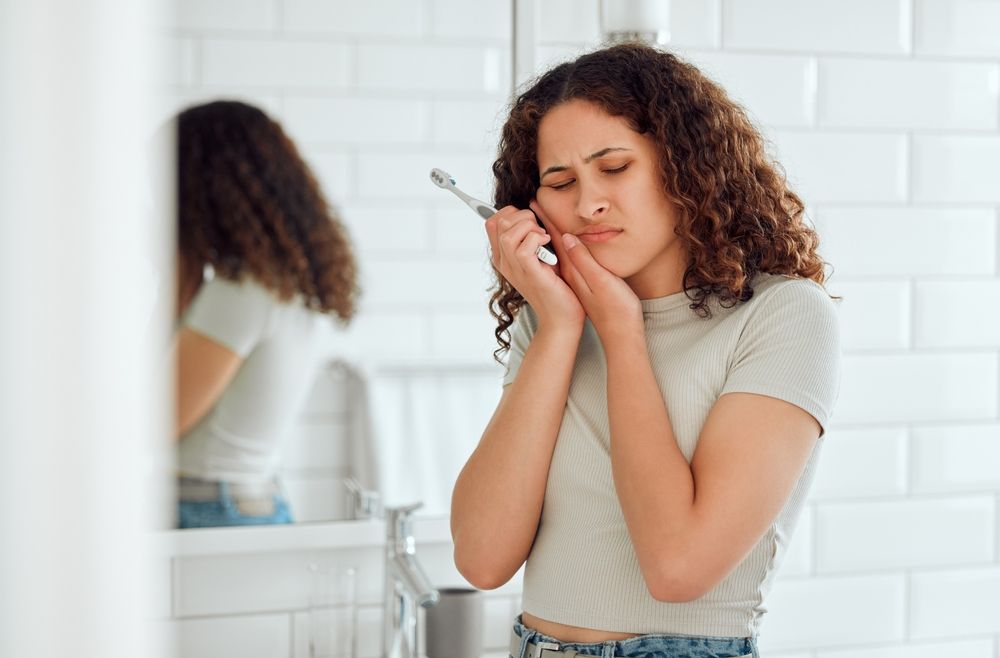
Tooth sensitivity is a common dental issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It involves discomfort or pain in the teeth as a response to certain stimuli, including temperatures and certain foods. This blog post will explore what tooth sensitivity is, identify its causes, and provide practical advice on how to manage and possibly reduce its occurrence.
What is Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity, also known as “dentin hypersensitivity,” occurs when the dentin, the softer part of the tooth that lies under the enamel and the gums, becomes exposed. The exposure of dentin leads to the sensitivity that is felt because this layer is connected directly to the nerve endings. When triggers such as hot, cold, sweet, or very acidic foods and drinks reach these nerve endings, it can result in a sharp, sudden burst of pain.
Causes of Tooth Sensitivity
Several factors contribute to the development of tooth sensitivity, including:
- Enamel Erosion: Over time, the enamel can wear away due to factors like brushing too hard, using a hard-bristled toothbrush, and the consumption of acidic foods and beverages.
- Gum Recession: This can expose the dentin at the root level. Gum disease and aggressive brushing are common causes of gum recession.
- Tooth Decay and Cavities: Decay that approaches the center of the tooth can cause sensitivity.
- Cracked Teeth: These can become filled with bacteria from plaque and cause inflammation and sensitivity.
- Teeth Grinding: This habit can wear down enamel and contribute to sensitivity.
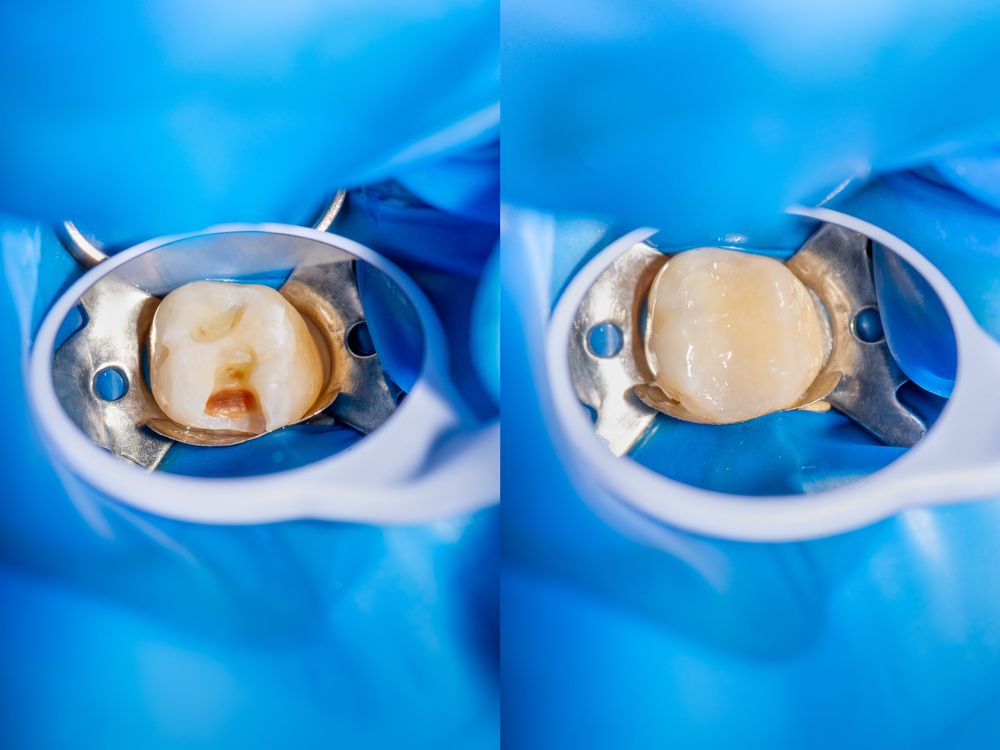
- Dental Procedures: Sensitivity can temporarily increase after procedures such as fillings, crowns, or teeth whitening.
Managing Tooth Sensitivity
The management of tooth sensitivity involves both home care and professional treatments. Here’s what you can do:
- Desensitizing Toothpaste: These toothpastes contain special ingredients that help block the transmission of pain signals from the surface of your tooth to the nerve. Regular use can gradually decrease sensitivity.
- Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing techniques can help prevent further enamel erosion and gum recession.
- Fluoride Application: Your dentist might apply fluoride to the sensitive areas of your teeth to strengthen enamel and reduce pain.
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding acidic foods and drinks like citrus fruits, soda, and wine can help prevent further enamel erosion.
- Dental Procedures: For more severe cases, your dentist might suggest inlays, bonding, or a gum graft to cover exposed roots and protect them from extreme temperatures.
- Mouthguards: If you grind your teeth, wearing a mouthguard at night can help reduce sensitivity by preventing further damage to your teeth.
When to See a Dentist
If your sensitivity is severe or does not improve with over-the-counter treatments, it is important to see a dentist. They can help identify the underlying cause of your sensitivity and suggest appropriate treatments. Additionally, regular dental check-ups can prevent the occurrence or worsening of tooth sensitivity by catching issues early.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while tooth sensitivity can be bothersome, it is usually manageable with the right approach. Understanding the causes and taking proactive steps to protect your teeth can help you achieve a healthier, more comfortable mouth.