A dental abscess, characterized by a collection of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection inside the tooth or gums, presents a significant and painful challenge to oral health. This condition not only causes severe discomfort but also poses a risk of spreading the infection to other parts of the body if left untreated. Understanding how to promptly and effectively manage a dental abscess is crucial in alleviating pain, halting the spread of infection, and preserving overall dental health. This guide aims to equip you with essential knowledge and practical steps to take when facing the distressing symptoms of a dental abscess, emphasizing the importance of immediate dental intervention, potential treatment options, and preventive measures to safeguard against future occurrences.
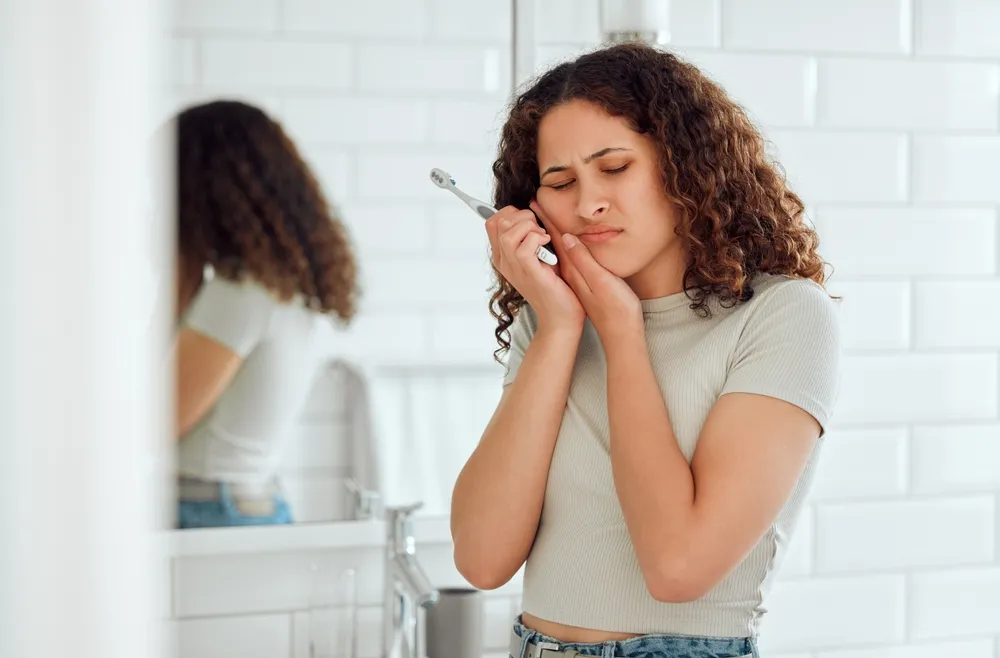
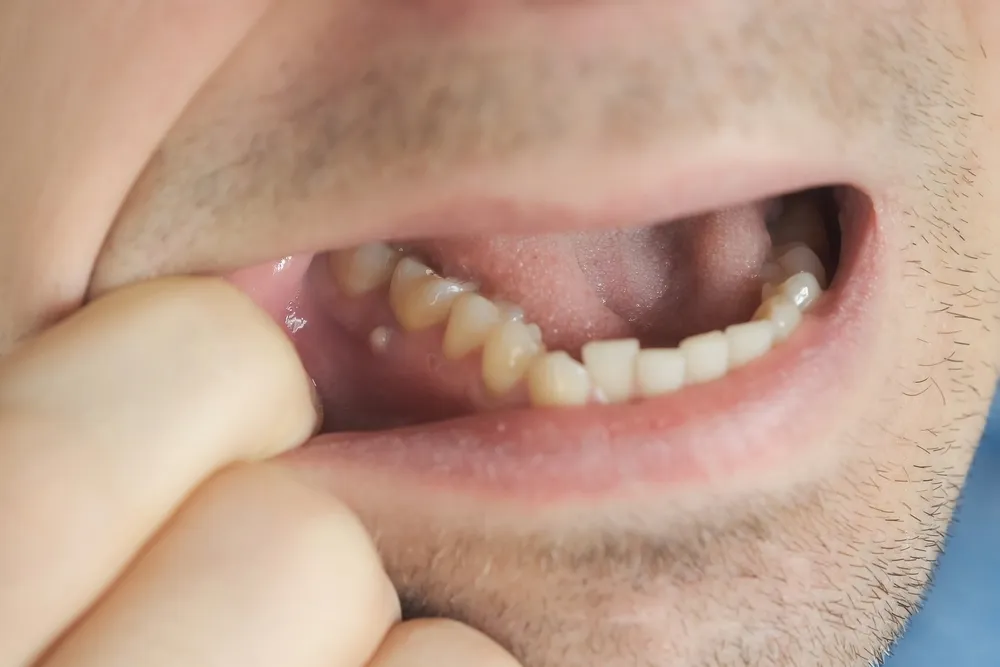
Recognize the Symptoms
First and foremost, it’s crucial to recognize the symptoms of a dental abscess, which may include:
- Severe, persistent, throbbing toothache that can radiate to the jawbone, neck, or ear
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Sensitivity to the pressure of chewing or biting
- Fever
- Swelling in your face or cheek
- Tender, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or in your neck
- Sudden rush of foul-tasting and smelling, salty fluid in your mouth and pain relief if the abscess ruptures
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing (in severe cases)
Seek Immediate Dental Care
If you suspect that you have a dental abscess, it’s crucial to seek immediate dental care. Abscesses do not go away on their own and can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious health complications. Your dentist will assess the abscess and determine the best course of treatment.
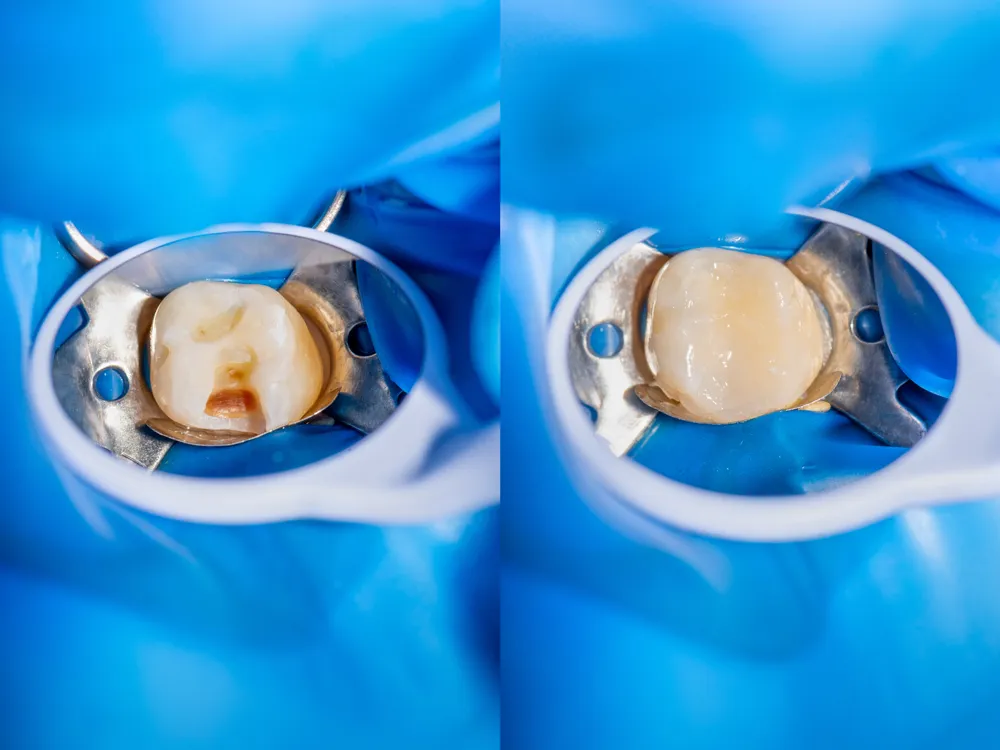
Treatment Options
The treatment for a dental abscess typically involves:

- Draining the Abscess: Your dentist may need to make a small cut into the abscess to drain the pus, which helps relieve pain and pressure.
- Performing a Root Canal: This procedure can help save your tooth by removing the infected pulp, draining the abscess, and then filling and sealing the tooth’s pulp chamber and root canals.
- Tooth Extraction: If the tooth cannot be saved, your dentist may recommend removing it to eliminate the source of the infection.
- Antibiotics: If the infection has spread beyond the abscessed area or if you have a weakened immune system, your dentist might prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection.
Home Care Tips
While you wait for your dental appointment, there are a few things you can do at home to ease the pain:
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water several times a day to help drain the abscess and relieve discomfort.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to help reduce the pain. Do not put painkillers directly against your gums as they may burn the tissue.
Prevention
Preventing a dental abscess starts with good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Also, limiting sugary foods and drinks can help prevent cavities, which are a leading cause of abscesses.
Conclusion
A dental abscess is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking immediate dental care can prevent the spread of the infection and preserve your oral health. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene is the key to preventing dental abscesses and ensuring a healthy, happy smile.