Maintaining good oral health is essential for a healthy smile and overall well-being. While most people are familiar with common dental issues like cavities and gum disease, there are other conditions that can affect our oral health. One such condition is dental tori, which refers to the bony growths that can develop in the mouth. In this blog, we will explore what dental tori are, their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
What Are Dental Tori?
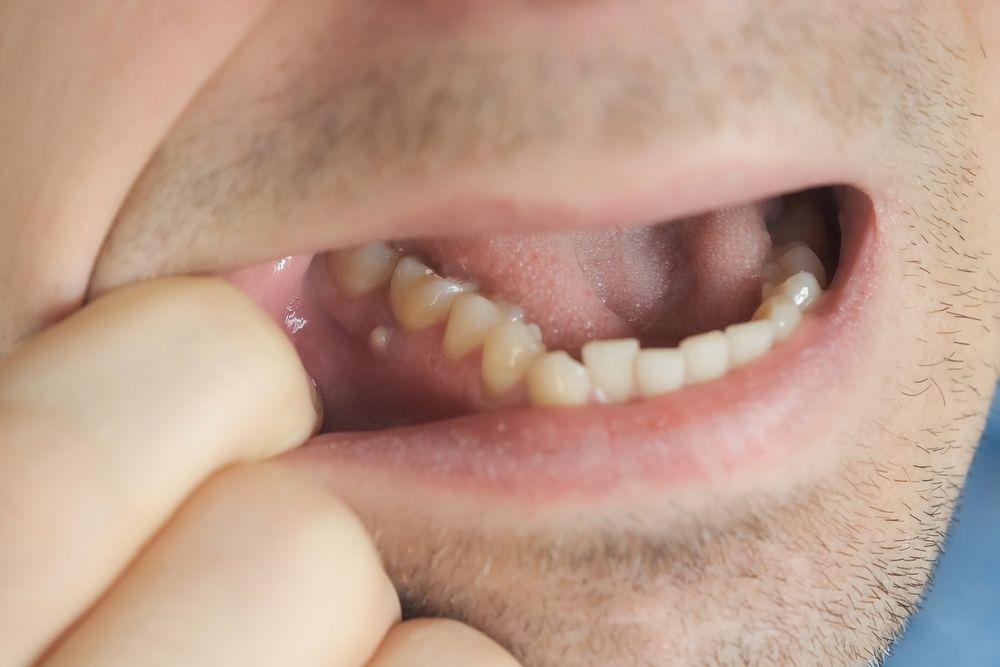
Dental tori, also known as torus (singular) or tori (plural), are bony growths that can occur in the mouth. They are non-cancerous and typically benign in nature. These bony outgrowths can develop on different areas within the oral cavity, including the roof of the mouth (palate), the lower jaw (mandible), and the outer surfaces of the upper or lower jaw (buccal area).

There are three primary types of dental tori:
- Torus palatinus (palatal tori): These are bony growths that appear on the midline of the hard palate, which is the roof of the mouth. Palatal tori can vary in size and shape and are often symmetrical, meaning they occur on both sides of the palate.
- Torus mandibularis (mandibular tori): These are bony growths that develop on the lingual side (inner aspect) of the lower jaw, specifically in the area where the premolars and molars are located. Mandibular tori can occur on one or both sides of the jaw.
- Buccal exostoses (buccal tori): These are bony growths that form on the outer surfaces of the upper or lower jaw, usually in the premolar and molar areas. Buccal tori are typically found on both sides of the jaw and can vary in size and shape.
It’s worth noting that dental tori can differ in appearance and size among individuals. They can range from small, barely noticeable bumps to larger protrusions. In many cases, dental tori are asymptomatic and do not cause any issues. However, depending on their size and location, they can occasionally interfere with oral hygiene practices, denture fitting, or orthodontic treatments.
If you suspect you have dental tori or have any concerns about oral growths, it is recommended to consult a dental professional for proper diagnosis and guidance. They can examine your mouth, determine the nature of the bony growths, and provide appropriate advice or treatment options if necessary.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of dental tori is not fully understood, but they can be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that genetics play a role in their development, as dental tori tend to run in families. Additionally, factors such as chronic teeth grinding (bruxism), certain lifestyle habits, and age can contribute to the formation of dental tori.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Dental tori are diagnosed through a comprehensive process that involves visual examination, palpation, and dental imaging techniques. During a dental examination, a dentist or oral healthcare professional visually inspects the mouth, paying close attention to areas such as the palate, lingual side of the lower jaw, and outer surfaces of the upper and lower jaws. They look for any signs of bony growths or irregularities. Palpation, which involves gently feeling the suspected areas, helps to assess the size, shape, and firmness of the tori. Additionally, dental imaging techniques like X-rays or cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans may be used to obtain detailed images of the tori. X-rays provide a two-dimensional view, allowing the dentist to evaluate the extent of the tori and their relationship to neighboring structures. CBCT scans offer a three-dimensional perspective, particularly useful for complex or larger tori and their proximity to critical structures. By combining these diagnostic approaches, dental professionals can accurately diagnose dental tori, determine the type of tori present, and assess any potential impact on oral health or treatment planning.
The treatment of dental tori depends on several factors, including the size, location, and presence of symptoms. In cases where dental tori are small and asymptomatic, no treatment may be necessary, and a “watch and wait” approach is often adopted. However, if the tori are causing discomfort, interfering with oral function, or affecting the fit of dental prosthetics or orthodontic treatments, treatment options may be considered. Surgical removal, known as tori reduction surgery, is a common approach. During the procedure, the excess bone growth is either removed or reshaped to alleviate symptoms and improve oral function. Tori reduction surgery is a safe and effective procedure, and the recovery period is typically short. It’s important to consult with a dental professional to evaluate the specific situation and determine the most appropriate treatment option for dental tori.
In Conclusion:
Dental tori are bony growths that can develop in the mouth, affecting oral health and function. While they may not always cause symptoms, it is important to be aware of their presence and seek professional advice if necessary. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal oral health. By working together with dental professionals, we can ensure the best possible care for dental tori and overall oral well-being.